A Flint index is ...
- Skipping Index: accelerate data scan by maintaining compact aggregate data structure which includes
- Partition: skip data scan by maintaining and filtering partitioned column value per file.
- MinMax: skip data scan by maintaining lower and upper bound of the indexed column per file.
- ValueSet: skip data scan by building a unique value set of the indexed column per file.
- BloomFilter: skip data scan by building a bloom filter of the indexed column per file.
- Covering Index: create index for selected columns within the source dataset to improve query performance
- Materialized View: enhance query performance by storing precomputed and aggregated data from the source dataset
Please see the following example in which Index Building Logic and Query Rewrite Logic column shows the basic idea behind each skipping index implementation.
| Skipping Index | Create Index Statement | Index Building Logic | Query Rewrite Logic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partition | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs ( year PARTITION, month PARTITION, day PARTITION, hour PARTITION ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT FIRST(year) AS year, FIRST(month) AS month, FIRST(day) AS day, FIRST(hour) AS hour, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 ) WHERE year = 2023 AND month = 4 |
| ValueSet | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs ( elb_status_code VALUE_SET ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT COLLECT_SET(elb_status_code) AS elb_status_code, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE elb_status_code = 404 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE ARRAY_CONTAINS(elb_status_code, 404) ) WHERE elb_status_code = 404 |
| MinMax | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs ( request_processing_time MIN_MAX ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT MIN(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_min, MAX(request_processing_time) AS request_processing_time_max, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE request_processing_time = 100 => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE request_processing_time_min <= 100 AND 100 <= request_processing_time_max ) WHERE request_processing_time = 100 |
| BloomFilter | CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs ( client_ip BLOOM_FILTER ) |
INSERT INTO flint_alb_logs_skipping_index SELECT BLOOM_FILTER_AGG(client_ip) AS client_ip, input_file_name() AS file_path FROM alb_logs GROUP BY input_file_name() |
SELECT * FROM alb_logs WHERE client_ip = '127.0.0.1' => SELECT * FROM alb_logs (input_files = SELECT file_path FROM flint_alb_logs_skipping_index WHERE BLOOM_FILTER_MIGHT_CONTAIN(client_ip, '127.0.0.1') ) WHERE client_ip = '127.0.0.1' |
- Auto Refresh:
- This feature allows the Flint Index to automatically refresh. Users can configure such as frequency of auto-refresh based on their preferences. There are two modes available for scheduling the auto-refresh:
- Internal Scheduler:
- Description: The data refresh is executed in micro-batch mode using the internal scheduler.
- Recommended Use-Case: This mode is ideal for low-latency use-cases where data needs to be refreshed frequently and quickly.
- External Scheduler:
- Description: The data refresh is executed using an external scheduler.
- Recommended Use-Case: This mode is suitable for scenarios where data responsiveness is less critical, helping to reduce the cost of maintaining a long-running Spark cluster.
- Manual Refresh:
- Users have the option to manually trigger a refresh for the Flint Index. This provides flexibility and control over when the refresh occurs.
- Full Refresh:
- Initiates a comprehensive update of the Flint Index, fetching all available data and ensuring the most up-to-date information is displayed.
- Incremental Refresh:
- Performs an incremental update by fetching only the new data since the last refresh. This is useful for optimizing the refresh process and reducing resource usage.
- Full Refresh:
- Users have the option to manually trigger a refresh for the Flint Index. This provides flexibility and control over when the refresh occurs.
The refresh mode is influenced by the index options specified during index creation, particularly the auto_refresh and incremental_refresh options. These options collectively define the behavior of the refresh mode when creating an index as below. Find more details in Create Index Options.
| Refresh Mode | auto_refresh | incremental_refresh |
|---|---|---|
| Auto Refresh | true | |
| Full Refresh | false | false |
| Incremental Refresh | false | true |
Currently, Flint metadata is only static configuration without version control and write-ahead log.
{
"version": "0.5.0",
"name": "...",
"kind": "skipping",
"source": "...",
"indexedColumns": [{
"kind": "...",
"columnName": "...",
"columnType": "..."
}],
"options": { },
"properties": { }
}For now, Flint Index doesn't define its own data type and uses OpenSearch field type instead.
| FlintDataType |
|---|
| boolean |
| binary |
| long |
| integer |
| short |
| byte |
| double |
| float |
| date |
| keyword |
| text |
| object |
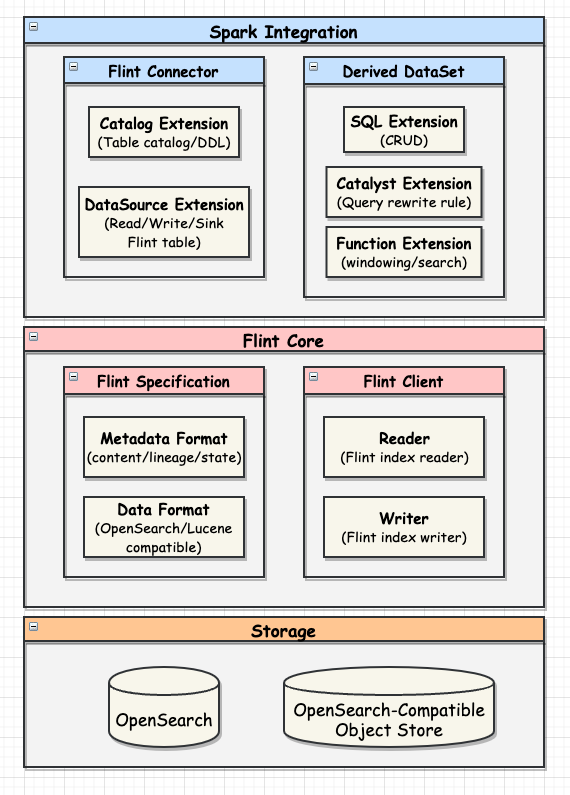
Please see Index Store section for more details.
FlintClient provides low-level Flint index management and data access API.
Index management API example:
// Initialized Flint client for a specific storage
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
FlintMetadata metadata = new FlintMetadata(...)
flintClient.createIndex("alb_logs_skipping_index", metadata)
flintClient.getIndexMetadata("alb_logs_skipping_index")Index data read and write example:
FlintClient flintClient = new FlintOpenSearchClient("localhost", 9200);
// read example
FlintReader reader = flintClient.createReader("indexName", null)\
while(reader.hasNext) {
reader.next()
}
reader.close()
// write example
FlintWriter writer = flintClient.createWriter("indexName")
writer.write("{\"create\":{}}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.write("{\"aInt\":1}")
writer.write("\n")
writer.flush()
writer.close()Flint index state transition:
High level API is dependent on query engine implementation. Please see Query Engine Integration section for details.
- CREATE: Create a Flint index with the specified indexing logic. If the auto-refresh option is enabled, a background job will continually update the index with the latest data from the source.
- REFRESH: Manually refresh a Flint index. This command is applicable only to indexes with the auto-refresh option disabled.
- SHOW: Display all Flint indexes in the specified catalog or source table.
- DESCRIBE: Retrieve detailed information about a Flint index.
- DROP: Delete a Flint index logically. This action stops the refreshing process and rules it out in query rewrite.
- VACUUM: Physically remove all data associated with a Flint index, including index metadata and data. This operation effectively cleans up and frees resources.
Provided below are the explanations for the parameters of the skipping algorithm. You can find the default values in the function signature below:
-
VALUE_SET(limit=100): If the column values of a file has higher cardinality than the limit (optional, default is 100), the value set will become null. This trade-off prevents excessive memory consumption at the expense of not skipping the file.
-
BLOOM_FILTER
-
BLOOM_FILTER(num_candidate=10, fpp=0.03): By default, the adaptive BloomFilter algorithm is used. Users can configure:
- The number of candidates (optional), starting with an expected number of distinct items at 1024 and doubling.
- The false positive probability of each candidate (optional).
- Examples:
BLOOM_FILTER,BLOOM_FILTER(20), BLOOM_FILTER(20, 0.01)
-
BLOOM_FILTER(false, num_items=10000, fpp=0.03): Setting the first parameter to
falsewill revert to the non-adaptive algorithm. Users can configure:- The expected number of distinct values (optional).
- The false positive probability (optional).
- Examples:
BLOOM_FILTER(false),BLOOM_FILTER(false, 1000000),BLOOM_FILTER(false, 1000000, 0.01)
-
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX [IF NOT EXISTS]
ON <object>
( column <skip_type> <skip_params> [, ...] )
WHERE <filter_predicate>
WITH ( options )
REFRESH SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
[DESC|DESCRIBE] SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
ALTER SKIPPING INDEX
ON <object>
WITH ( options )
DROP SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
VACUUM SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
ANALYZE SKIPPING INDEX ON <object>
<object> ::= [db_name].[schema_name].table_nameSkipping index type consists of skip type name and optional parameters
<skip_type> ::= { PARTITION, VALUE_SET, MIN_MAX }
<skip_params> := ( param1, param2, ... )Example:
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
(
time PARTITION,
elb_status_code VALUE_SET,
client_ip VALUE_SET(20),
request_processing_time MIN_MAX
)
WHERE time > '2023-04-01 00:00:00'
REFRESH SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
DESCRIBE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
ALTER SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
WITH ( auto_refresh = false )
DROP SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs
VACUUM SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logsCREATE INDEX [IF NOT EXISTS] name ON <object>
( column [, ...] )
WHERE <filter_predicate>
WITH ( options )
REFRESH INDEX name ON <object>
SHOW [INDEX|INDEXES] ON <object>
[DESC|DESCRIBE] INDEX name ON <object>
ALTER INDEX name ON <object>
WITH ( options )
DROP INDEX name ON <object>
VACUUM INDEX name ON <object>Example:
CREATE INDEX elb_and_requestUri
ON alb_logs ( elb, requestUri )
REFRESH INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
SHOW INDEX ON alb_logs
DESCRIBE INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
ALTER INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
WITH ( auto_refresh = false )
DROP INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logs
VACUUM INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON alb_logsCREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW [IF NOT EXISTS] name
AS <query>
WITH ( options )
REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW name
SHOW MATERIALIZED [VIEW|VIEWS] IN catalog[.database]
[DESC|DESCRIBE] MATERIALIZED VIEW name
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW name
WITH ( options )
DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW name
VACUUM MATERIALIZED VIEW nameExample:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics
AS
SELECT
window.start AS startTime,
COUNT(*) AS count
FROM alb_logs
GROUP BY TUMBLE(time, '1 Minute')
REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics
SHOW MATERIALIZED VIEWS IN spark_catalog.default
DESC MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics
WITH ( auto_refresh = false )
DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics
VACUUM MATERIALIZED VIEW alb_logs_metrics- Show Flint Indexes: Displays all the flint indexes with their info. It outputs the following columns:
- flint_index_name: the full OpenSearch index name
- kind: type of the index (skipping / covering / mv)
- database: database name for the index
- table: table name for skipping and covering index
- index_name: user defined name for covering index and materialized view
- auto_refresh: auto refresh option of the index (true / false)
- status: status of the index
SHOW FLINT [INDEX|INDEXES] IN catalog[.database]Example:
sql> SHOW FLINT INDEXES IN spark_catalog.default;
fetched rows / total rows = 3/3
+-------------------------------------------------------------+----------+----------+-----------+-----------------+--------------+------------+
| flint_index_name | kind | database | table | index_name | auto_refresh | status |
|-------------------------------------------------------------+----------+----------+-----------+-----------------+--------------+------------|
| flint_spark_catalog_default_http_count_view | mv | default | NULL | http_count_view | false | active |
| flint_spark_catalog_default_http_logs_skipping_index | skipping | default | http_logs | NULL | true | refreshing |
| flint_spark_catalog_default_http_logs_status_clientip_index | covering | default | http_logs | status_clientip | false | active |
+-------------------------------------------------------------+----------+----------+-----------+-----------------+--------------+------------+
- Analyze Skipping Index: Provides recommendation for creating skipping index. It outputs the following columns:
- column_name: recommended column's name
- column_type: recommended column's type
- skipping_type: recommended skipping type for column
- reason: why this skipping type is recommended
ANALYZE SKIPPING INDEX ON [catalog.database.]tableExample:
sql> ANALYZE SKIPPING INDEX ON alb_logs;
fetched rows / total rows = 5/5
+-------------------------+-------------+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| column_name | column_type | skipping_type | reason |
|-------------------------+-------------+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
| year | integer | PARTITION | PARTITION data structure is recommended for partition columns |
| month | integer | PARTITION | PARTITION data structure is recommended for partition columns |
| day | integer | PARTITION | PARTITION data structure is recommended for partition columns |
| request_processing_time | integer | MIN_MAX | MIN_MAX data structure is recommended for IntegerType columns |
| client_ip | string | BLOOM_FILTER | BLOOM_FILTER data structure is recommended for StringType columns |
+-------------------------+-------------+---------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------+
User can provide the following options in WITH clause of create statement:
auto_refresh: default value is false. Automatically refresh the index if set to true. Otherwise, user has to trigger refresh byREFRESHstatement manually.scheduler_mode: A mode string (internalorexternal) that describes howauto_refreshis scheduled.checkpoint_locationis required for the external scheduler.refresh_interval: a string as the time interval for incremental refresh, e.g. 1 minute, 10 seconds. This is only applicable when auto refresh enabled. Please checkorg.apache.spark.unsafe.types.CalendarIntervalfor valid duration identifiers. By default, next micro batch will be generated as soon as the previous one complete processing.incremental_refresh: default value is false. incrementally refresh the index if set to true. Otherwise, fully refresh the entire index. This only applicable when auto refresh disabled.checkpoint_location: a string as the location path for refresh job checkpoint (auto or incremental). The location has to be a path in an HDFS compatible file system and only applicable when auto refresh enabled. If unspecified, temporary checkpoint directory will be used and may result in checkpoint data lost upon restart.watermark_delay: a string as time expression for how late data can come and still be processed, e.g. 1 minute, 10 seconds. This is required by auto and incremental refresh on materialized view if it has aggregation in the query.output_mode: a mode string that describes how data will be written to streaming sink. If unspecified, default append mode will be applied.index_settings: a JSON string as index settings for OpenSearch index that will be created. Please follow the format in OpenSearch documentation. If unspecified, default OpenSearch index settings will be applied.extra_options: a JSON string as extra options that can be passed to Spark streaming source and sink API directly. Use qualified source table name (because there could be multiple) and "sink", e.g. '{"sink": "{key: val}", "table1": {key: val}}'
Note that the index option name is case-sensitive. Here is an example:
WITH (
auto_refresh = true,
refresh_interval = '10 Seconds',
checkpoint_location = 's3://test/',
watermark_delay = '1 Second',
output_mode = 'complete',
index_settings = '{"number_of_shards": 2, "number_of_replicas": 3}',
extra_options = '{"spark_catalog.default.alb_logs": {"maxFilesPerTrigger": "1"}}'
)Example:
CREATE INDEX elb_and_requestUri
ON alb_logs ( elb, requestUri )
WITH (
auto_refresh = true,
refresh_interval = '1 minute',
checkpoint_location = 's3://test/'
)User can provide the following options in WITH clause of alter statement:
auto_refresh: This is required for alter statement. Currently, we restrict that an alter statement must change the auto refresh option from its original value.refresh_intervalincremental_refreshcheckpoint_locationwatermark_delay
Currently Flint index job ID is same as internal Flint index name in OpenSearch section below.
- Recover Job: Initiates a restart of the index refresh job and transition the Flint index to the 'refreshing' state. Additionally, it includes functionality to clean up the metadata log entry in the event that the Flint data index is no longer present in OpenSearch.
RECOVER INDEX JOB <id>Example:
RECOVER INDEX JOB `flint_spark_catalog_default_test_skipping_index`OpenSearch index corresponding to the Flint index follows the naming convention below:
- Skipping index:
flint_[catalog_database_table]_skipping_index - Covering index:
flint_[catalog_database_table]_[index_name]_index - Materialized view:
flint_[catalog_database_table]_[mv_name]
It's important to note that any uppercase letters in the index name and table name (catalog, database and table) in SQL statement will be automatically converted to lowercase due to restriction imposed by OpenSearch.
Examples:
-- OpenSearch index name is `flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_skipping_index`
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON spark_catalog.default.alb_logs ...
-- OpenSearch index name is `flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_elb_and_requesturi_index`
CREATE INDEX elb_and_requestUri ON spark_catalog.default.alb_logs ...In the index mapping, the _meta and propertiesfield stores meta and schema info of a Flint index.
{
"_meta": {
"version": "0.1",
"indexConfig": {
"kind": "skipping",
"properties": {
"indexedColumns": [
{
"kind": "Partition",
"columnName": "year",
"columnType": "int"
},
{
"kind": "ValuesSet",
"columnName": "elb_status_code",
"columnType": "int"
}
]
}
},
"source": "alb_logs"
},
"properties": {
"year": {
"type": "integer"
},
"elb_status_code": {
"type": "integer"
},
"file_path": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}spark.datasource.flint.host: default is localhost.spark.datasource.flint.port: default is 9200.spark.datasource.flint.scheme: default is http. valid values [http, https]spark.datasource.flint.auth: default is noauth. valid values [noauth, sigv4, basic]spark.datasource.flint.auth.username: basic auth username.spark.datasource.flint.auth.password: basic auth password.spark.datasource.flint.region: default is us-west-2. only been used when auth=sigv4spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider: default is empty.spark.datasource.flint.write.id_name: no default value.spark.datasource.flint.ignore.id_column: default value is true.spark.datasource.flint.write.batch_size: "The number of documents written to Flint in a single batch request. Default value is Integer.MAX_VALUE.spark.datasource.flint.write.batch_bytes: The approximately amount of data in bytes written to Flint in a single batch request. The actual data write to OpenSearch may more than it. Default value is 1mb. The writing process checks after each document whether the total number of documents (docCount) has reached batch_size or the buffer size has surpassed batch_bytes. If either condition is met, the current batch is flushed and the document count resets to zero.spark.datasource.flint.write.refresh_policy: default value is false. valid values [NONE(false), IMMEDIATE(true), WAIT_UNTIL(wait_for)]spark.datasource.flint.read.scroll_size: default value is 100.spark.datasource.flint.read.scroll_duration: default value is 5 minutes. scroll context keep alive duration.spark.datasource.flint.retry.max_retries: max retries on failed HTTP request. default value is 3. Use 0 to disable retry.spark.datasource.flint.retry.http_status_codes: retryable HTTP response status code list. default value is "429,502" (429 Too Many Request and 502 Bad Gateway).spark.datasource.flint.retry.exception_class_names: retryable exception class name list. by default no retry on any exception thrown.spark.flint.optimizer.enabled: default is true. enable the Flint optimizer for improving query performance.spark.flint.optimizer.covering.enabled: default is true. enable the Flint covering index optimizer for improving query performance.spark.flint.index.hybridscan.enabled: default is false.spark.flint.index.checkpoint.mandatory: default is true.spark.datasource.flint.socket_timeout_millis: default value is 60000.spark.flint.monitor.initialDelaySeconds: Initial delay in seconds before starting the monitoring task. Default value is 15.spark.flint.monitor.intervalSeconds: Interval in seconds for scheduling the monitoring task. Default value is 60.spark.flint.monitor.maxErrorCount: Maximum number of consecutive errors allowed before stopping the monitoring task. Default value is 5.
The following table define the data type mapping between Flint data type and Spark data type.
| FlintDataType | SparkDataType |
|---|---|
| boolean | BooleanType |
| long | LongType |
| integer | IntegerType |
| short | ShortType |
| byte | ByteType |
| double | DoubleType |
| float | FloatType |
| date(Timestamp) | DateType |
| date(Date) | TimestampType |
| keyword | StringType, VarcharType, CharType |
| text | StringType(meta(osType)=text) |
| object | StructType |
- Currently, Flint data type only support date. it is mapped to Spark Data Type based on the format:
- Map to DateType if format = strict_date, (we also support format = date, may change in future)
- Map to TimestampType if format = strict_date_optional_time_nanos, (we also support format = strict_date_optional_time | epoch_millis, may change in future)
- Spark data types VarcharType(length) and CharType(length) are both currently mapped to Flint data type keyword, dropping their length property. On the other hand, Flint data type keyword only maps to StringType.
Unsupported Spark data types:
- DecimalType
- BinaryType
- YearMonthIntervalType
- DayTimeIntervalType
- ArrayType
- MapType
Here is an example for Flint Spark integration:
val flint = new FlintSpark(spark)
// Skipping index
flint.skippingIndex()
.onTable("spark_catalog.default.alb_logs")
.filterBy("time > 2023-04-01 00:00:00")
.addPartitions("year", "month", "day")
.addValueSet("elb_status_code")
.addMinMax("request_processing_time")
.addBloomFilter("client_ip")
.create()
flint.refreshIndex("flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_skipping_index")
// Covering index
flint.coveringIndex()
.name("elb_and_requestUri")
.onTable("spark_catalog.default.alb_logs")
.addIndexColumns("elb", "requestUri")
.create()
flint.refreshIndex("flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_elb_and_requestUri_index")
// Materialized view
flint.materializedView()
.name("spark_catalog.default.alb_logs_metrics")
.query("SELECT ...")
.create()
flint.refreshIndex("flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_metrics")
flint.deleteIndex("flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_skipping_index")
flint.vacuumIndex("flint_spark_catalog_default_alb_logs_skipping_index")Flint Spark index state transition:
trait FlintSparkSkippingStrategy {
TODO: outputSchema, getAggregators, rewritePredicate
}Here is an example for read index data from AWS OpenSearch domain.
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.host", "yourdomain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.port", "-1")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.scheme", "https")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.auth", "sigv4")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.region", "us-west-2")
spark.conf.set("spark.datasource.flint.refresh_policy", "wait_for")
val df = spark.range(15).toDF("aInt")
val re = df.coalesce(1)
.write
.format("flint")
.mode("overwrite")
.save("t001")
val df = new SQLContext(sc).read
.format("flint")
.load("t001")
TODO
Due to the conversion of uppercase letters to lowercase in OpenSearch index names, it is not permissible to create a Flint index with a table name or index name that differs solely by case.
For instance, only one of the statement per group can be successfully:
-- myGlue vs myglue
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON myGlue.default.alb_logs ...
CREATE SKIPPING INDEX ON myglue.default.alb_logs ...
-- idx_elb vs Idx_elb
CREATE INDEX idx_elb ON alb_logs ...
CREATE INDEX Idx_elb ON alb_logs ...For now, only single or conjunct conditions (conditions connected by AND) in WHERE clause can be optimized by skipping index.
Flint use DefaultAWSCredentialsProviderChain. When running in EMR Spark, Flint use executionRole credentials
--conf spark.jars.packages=org.opensearch:opensearch-spark-standalone_2.12:0.5.0-SNAPSHOT \
--conf spark.jars.repositories=https://aws.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.executorEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.host=opensearch-domain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.port=-1 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.scheme=https \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth=sigv4 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.region=us-west-2 \
- In AccountB, add trust relationship to arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::AccountA:role/JobExecutionRoleA"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
- In AccountA, add STS assume role permission to arn:aws:iam::AccountA:role/JobExecutionRoleA
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB"
}
]
}
- Set the spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider property with value as com.amazonaws.emr.AssumeRoleAWSCredentialsProvider. Set the environment variable ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN with the ARN value of CrossAccountRoleB.
--conf spark.jars.packages=org.opensearch:opensearch-spark-standalone_2.12:0.5.0-SNAPSHOT \
--conf spark.jars.repositories=https://aws.oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.executorEnv.JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-17-amazon-corretto.x86_64 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.host=opensearch-domain.us-west-2.es.amazonaws.com \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.port=-1 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.scheme=https \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth=sigv4 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.region=us-west-2 \
--conf spark.datasource.flint.customAWSCredentialsProvider=com.amazonaws.emr.AssumeRoleAWSCredentialsProvider \
--conf spark.emr-serverless.driverEnv.ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::AccountB:role/CrossAccountRoleB \
--conf spark.executorEnv.ASSUME_ROLE_CREDENTIALS_ROLE_ARN=arn:aws:iam::AccountBB:role/CrossAccountRoleB
Add Basic Auth configuration in Spark configuration. Replace username and password with correct one.
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth=basic
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth.username=username
--conf spark.datasource.flint.auth.password=password